Introduction
The digital transformation is leading the way in wearable technology and mobile sensing, which are transforming our environment and our interactions with it. These developments go well beyond fitness trackers and smartwatches; they include a wide range of uses, such as environmental sensing and health monitoring, that improve productivity, safety, and general quality of life. The effect, uses, and future prospects of wearable technology and mobile sensing are examined in-depth in this article.
The Evolution of Wearable Technology
Electronic gadgets made to be worn on the body and easily incorporated into daily life are referred to as wearable technology. Wearable technology started out as basic pedometers and has since developed into sophisticated gadgets that can do a wide range of intricate activities. Athlete heart rate monitors and wristwatches with modest computing capabilities are two early examples. The introduction of smartphones, which offered the connection and computing capacity required to support more sophisticated wearables, was the true breakthrough, though.
These days, wearable technology includes anything from fitness trackers, smart glasses, and smartwatches to more specialized medical equipment like glucose monitors and ECG sensors. Numerous sensors on these gadgets gather information on a range of topics, including as heart rate, exercise, sleep habits, and even environmental aspects like UV exposure and air quality.
The Role of Mobile Sensing
Mobile sensing is the process of gathering and analyzing data about the user and the environment using sensors that are built into mobile devices. Smartphones are strong mobile sensing platforms since they come with gyroscopes, GPS, accelerometers, cameras, and microphones. These sensors provide a multitude of information that may be used for a wide range of applications by tracking movement, orientation, position, and ambient conditions.
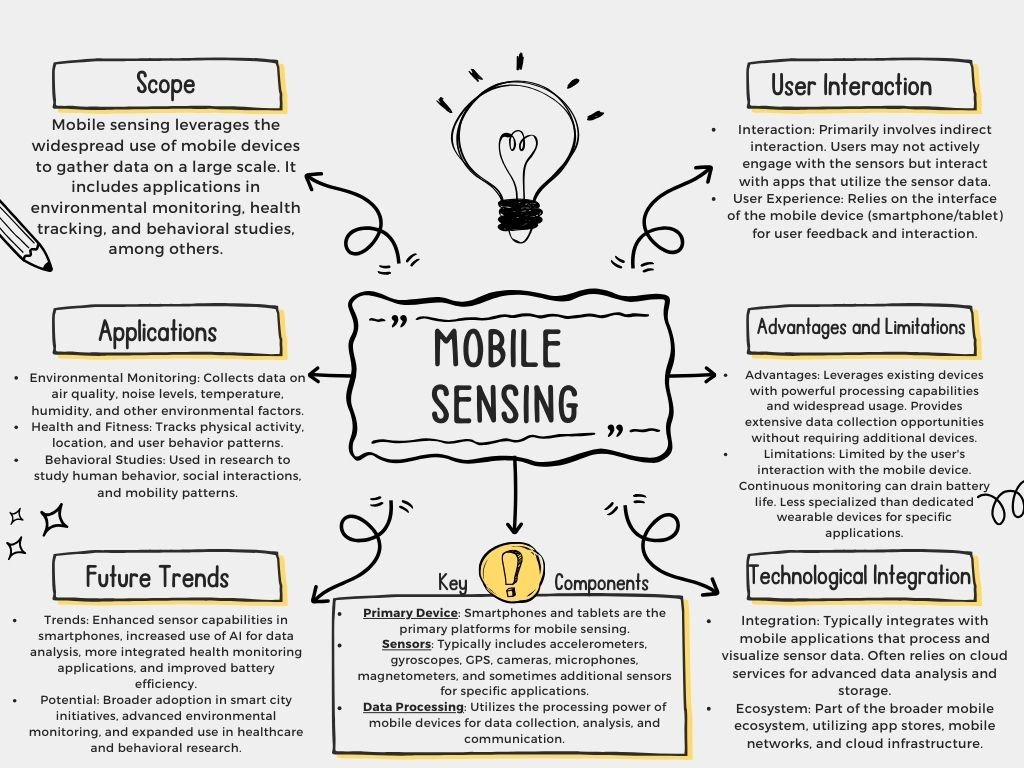
Applications of Wearable Technology and Mobile Sensing
1. Healthcare and Fitness:
Fitness and healthcare have advanced significantly as a result of wearable technologies and mobile sensing. Fitness trackers and smartwatches track heart rate, sleep habits, and physical activity, giving users important health data and motivating them to lead better lives. Wearable medical technology has the potential to manage drug adherence, monitor chronic disorders, and potentially identify early warning indicators of disease. For example, wearable ECG monitors can identify abnormal heartbeats and notify users to seek medical assistance; continuous glucose monitors help diabetic patients regulate their blood sugar levels in real-time.
2. Environmental Monitoring:
Environmental monitoring relies heavily on mobile sensing. Environmental policy and public health choices can be informed by real-time data from temperature, humidity, UV exposure, and air quality measurements provided by smartphones and wearable technology. Mobile sensing apps, for instance, may identify urban pollution hotspots and assist authorities in putting targeted measures in place.
3. Workplace Safety and Productivity:
Wearable technology improves job efficiency and safety in industrial environments. By monitoring workers’ vital signs and identifying potentially dangerous situations, wearable technology lowers the likelihood of mishaps and injuries. Exoskeletons can help with heavy lifting, decreasing physical strain and preventing musculoskeletal injuries, while smart helmets with sensors can warn workers of possible hazards.
4. Augmented and Virtual Reality:
We are seeing a revolution in the way we engage with digital information because to wearable technology like VR headsets and smart glasses. By superimposing digital data on the real environment, augmented reality (AR) has the potential to improve learning outcomes in the field of education. VR headsets provide immersive entertainment experiences that let users explore virtual worlds. These technologies may also be used in professional training, allowing for accurate simulations in disciplines like engineering, aviation, and medicine.
5. Personal Safety and Security:
Personal security and safety can be improved using wearable technologies. In the event of an emergency, wearable panic buttons can notify police or specified contacts, while smartwatches equipped with GPS tracking can assist in locating persons. Furthermore, wearables that use biometric authentication—like fingerprint or face recognition—offer secure access to apps and devices while safeguarding private data.
Challenges and Considerations
- Wearable technology and mobile sensing have many advantages, but they also have drawbacks. The main issues are privacy and data security because these gadgets gather private and sensitive data. To win consumers’ confidence and safeguard their privacy, it is essential to make sure that data is sent and kept securely.
- Battery life is another problem. Because wearable technology must be comfortable and lightweight, the size of its batteries must be constrained. Developments in energy-efficient sensors and low-power circuits are necessary to increase battery life and make these gadgets more useful for daily usage.
- Standardization and interoperability are also crucial factors. Ensuring the smooth communication and data sharing of an increasing number of devices and platforms is crucial for their general acceptance and efficacy. Creating uniform guidelines and procedures can help to achieve interoperability.
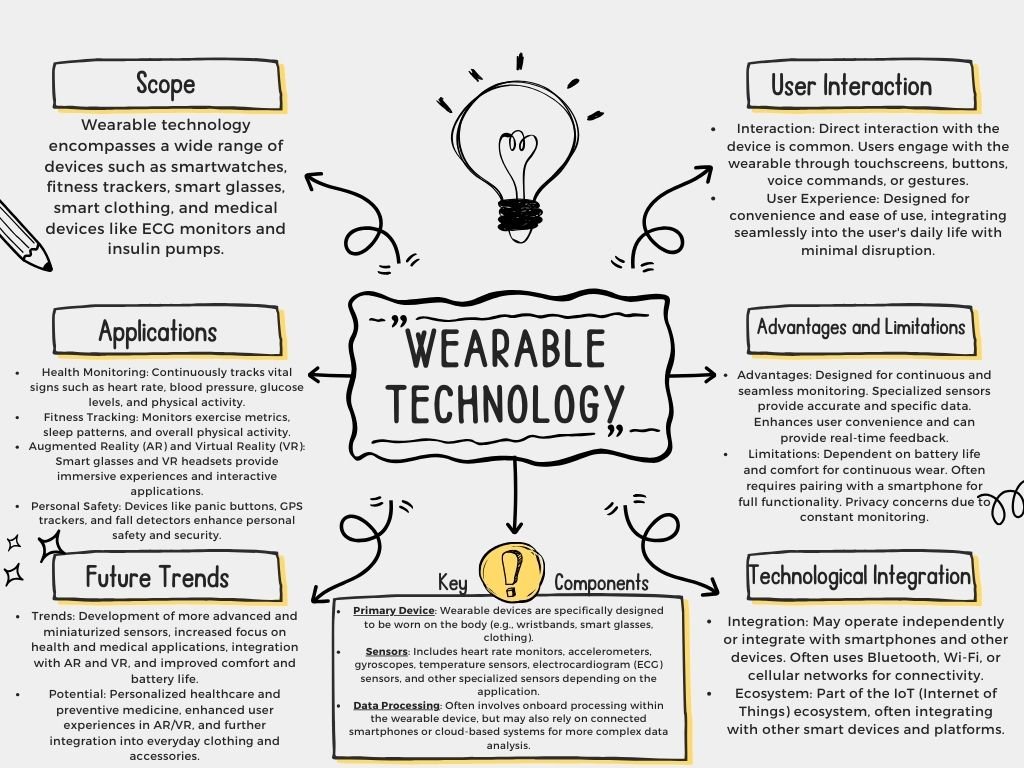
The Future of Wearable Technology and Mobile Sensing
- With continuous developments in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and sensor technologies, wearable technology and mobile sensing have a bright future. The creation of increasingly complex and compact sensors is one emerging trend that is opening up new applications and enhancing those that already exist. For instance, it is possible to include stretchy and flexible sensors into garments to provide ongoing health monitoring without the need for separate equipment.
- Processing the enormous volumes of data produced by wearable technology and mobile sensors is largely dependent on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Real-time data analysis is possible with these technologies, which can produce individualized insights and suggestions. AI systems, for example, are able to identify trends in health data and anticipate possible problems before they become significant ones.
- Initiatives aimed at creating smart cities are also anticipated to include wearable technology and mobile sensors increasingly. Cities may optimize resource management, improve public services, and raise resident quality of life by merging data from several sensors and devices. For instance, intelligent waste management systems may improve collection routes and lessen their negative effects on the environment, while intelligent traffic management systems can lower emissions and congestion.
Our daily lives, workplaces, and interactions with our surroundings are being completely transformed by wearable technology and mobile sensing. These technologies have a wide range of uses and advantages, from environmental monitoring and personal safety to healthcare and fitness. The influence of wearable technology and mobile sensing on our everyday lives will be further enhanced as breakthroughs in AI and the creation of more advanced sensors open up new opportunities. Even if there are still obstacles to overcome, these technologies have the potential to significantly enhance productivity, well-being, safety, and health, making them a powerful and revolutionary force in the digital age.
In Conclusion

Biden believes there will be “fair election” He is concerned, though
Biden Confident About Election Fairness but Concerned Over Peaceful Transition: Key Insights Ahead of 2024 President Joe Biden has offered a cautious and optimistic assessment

Kremlin Brushes Off U.S. Political Debates on Putin, Focuses on Sovereignty
Political tensions are escalating in the United States as the 2024 presidential election draws near, with contenders sharply criticizing one another’s programs. A recent verbal

Kamala Harris challenges Trump in a CNN interview with Walz, addressing her tendency to flip-flop
In her first in-depth interview since being announced as the Democratic Party’s 2024 presidential contender, Vice President Kamala Harris defended her shifting views on climate

Protect your phone from threats and Viruses: Precautions, Cautions, and Solutions
With everything being digitally connected these days, cellphones have become a necessity in our daily lives. They act as our financial managers, personal assistants, and

Mumbai Citezn woman spends Rs 9.4 lakh on Starbucks coffee orders From Zomato
In India Zomato Celebrates “Mumbai Woman’s ₹9.4 Lakh Starbucks” ? In a world where coffee lovers are known to splurge on their favorite brews, one

Economic Impacts on the Citrus Industry: Florida, California’s in 2024
Economic Impacts on the Citrus Industry : Citrus greening has significant negative effects on the economy. Growers are obliged to replace and remove diseased trees as



